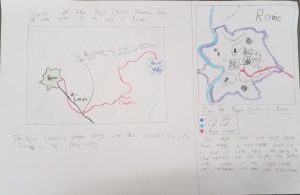
Aqueducts were perhaps the greatest achievement of Roman engineers, since they supplied water to the masses, and increased hygiene for all Roman citizens. Aqueducts were constructed as public works throughout the Roman Empire, but the greatest and most plentiful brought their water into Rome. Some people wonder why many European civilizations in the Middle Ages, after the Roman Empire, but this project highlights the level of planning and engineering that had to go into the aqueducts.
We chose to base our blueprints (seen above) on the Aqua Claudia, one of Rome’s most ambitious projects. Our blueprints show the basic dimensions of the Aqua Claudia, as well as the facts and uses for these parts. Some interesting things were the use of siphons. Romans would typically use taller bridges over valleys whenever possible, however it was not always possible with the mountainous regions of Italy. Siphons are still used today; they work by using pressure and gravity, as well as sealed pipes to keep the pressure, to push the water up the other side of the valley. A simple description of the siphon and how it works, but if you are still confused there’s more information here.
In conclusion, Roman aqueducts, and the Aqua Claudia in particular, were breathtaking public works and incredible feats of engineering for the time of Rome. They greatly improved Roman health, quality of life and the beauty and riches of Rome.